There is a lot of buzz around blockchain and hashgraph technology. Blockchain and hashgraph are two very different technologies with unique benefits. Blockchain is well-known and often used to refer to all distributed ledger technologies. Hashgraph is a somewhat new player in the space that offers some unique advantages. This blog post will look at the critical differences between blockchain and hashgraph technologies.
What Is Blockchain Technology? How Does It Work?
This technology is also referred to as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). It can be best described as an open record book distributed on multiple computers, where all the records must agree with the others before any of them are changed.
The widely known blockchain technology was introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin. The key benefits behind it are that it’s decentralized, secure, and transparent for all involved parties. A block of information is validated every 10 minutes using millions of processors across hundreds of thousands of servers worldwide through a process called mining. That is why more and more corporations are discovering ways to utilize blockchain technology, and this is why we are seeing an increase in the number of blockchain development companies.
Blockchain technology was originally used to track transactions involving cryptocurrencies like bitcoin or Ethereum. Its potential use cases go far beyond digital currencies. Blockchains have been applied to topics like land registries, voting records, and supply chain management.
How does Blockchain Technology Work?
The security of the blockchain is a result of its decentralized nature. The record book is stored on thousands of computers simultaneously, so no single entity can ever take control. Even if one computer were to be hacked or attacked, the information on the other nodes would remain valid because all of them would need to agree before adding a new block.
Since this was originally developed for digital currencies, it also requires that each transaction is validated by multiple parties independently before being added to the blockchain forever. When someone wants to spend cryptocurrency, they broadcast their intention to everyone else in the network (usually via wallet software). Miners then group transactions into “blocks” and add them to the blockchain one by one.
Blockchain technology also requires that all transactions be pre-approved or “validated” before they can go through. This is why it’s often referred to as a “permissionless” ledger. It ensures that no transaction can ever take place without being validated by anyone in the network, so there’s no need for a central authority.
It is generally a good thing for security. Combining permission less with decentralized ledgers makes it impossible for any validation logic to be executed before a block containing transactions is added to the chain. So if you want to update something within a shared database, say change an address on your driver’s license, you have to request everyone else to validate that change after it’s made. This makes blockchain technology cumbersome to use for certain applications where things need to be verified before they’re added (such as with driver’s licenses).
To expand on this further, some of the major issues with using blockchains are:
1. Slow performance
A huge amount of computing power is needed to mine blocks, taking 10 minutes or more per transaction. That means you have to wait at least that long every time you want to send anything. Compare that to Visa credit card transactions which complete in seconds, and you’ll see why many people consider this a big bottleneck for blockchain technology.
2. High cost
Mining requires expensive hardware and consumes huge amounts of electricity since these computers constantly work, solving computationally-intensive problems. The hardware and electricity costs result in a very high transaction fee that can be as much as $20 per transaction.
3. Centralization
Since mining is so resource-intensive, it has become concentrated in countries with cheap sources of electricity like China, Iceland, or Venezuela, where you have to trust the government might not take control one day and shut down all transactions. In addition, about five companies dominate most of the market for cryptocurrency mining equipment which further adds to its centralized nature.
4. Lack of banks
While this was originally designed to decentralize currency from banks and governments (hence “crypto” currency), you still need access to a bank account if your country supports it (like the US). If you want to send a transaction to someone who is not in your country, you’ll need a bank account on their end as well. With hashgraph technology, this is no longer necessary.
5. Poor governance
There’s very little that can be done to upgrade the system without hard forking. It involves undoing everything on all nodes and starting from scratch. Ethereum’s experience with The DAO fork is an example of how messy these processes can get as the community bickered over how best to address it. This has led some people to believe that there is little flexibility or room for improvement. That’s if things go wrong with blockchain technology. [/acd_list]
What Is Hashgraph Technology?
Hashgraph is a consensus algorithm that uses the process of collecting and agreeing on transactions and validating them. It claims to be superior to the blockchain by solving the issues of speed and fairness found in blockchain technology, such as:
- Speed – Hashgraph can achieve up to 250 000+ transactions per second (fps) compared to only 10–25tps for Ethereum and 3–7tps for Bitcoin.
- Fairness – Hashgraph has no need for an energy-hungry proof-of-work protocol like bitcoin. This ensures that anyone trying to fork the ledger will not have enough computing power be able to overtake the main node.
Hashgraph is gaining popularity with many organizations all over the world, such as Barclays Bank, HSBC, and Toyota. Swirlds has created a technology that allows it to be used in the real world and has partnered with companies such as CULedger (Credit Union) and VISA for its coin offering.
How Does Hashgraph Work?
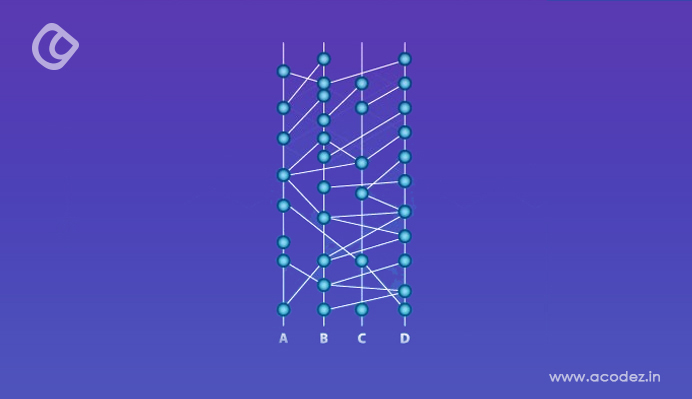
Hashgraph is a fast, secure, open-source, public ledger that can record transactions or any digital events in a fair and efficient way. It is much faster than blockchain and more secure thanks to its asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) consensus model and Virtual Voting. Also, Hashgraph doesn’t need mining which means no fees or energy waste when sending transactions across the network. This all leads to what looks like a fairer consensus compared to blockchains, where computing power determines who has control over the network.
Hashgraph is a distributed ledger technology that works as follows: transactions take place within “swarms,” which are groups of nodes that exchange data about the latest transactions and then reach a consensus on what each node will include in their next transaction. Hashgraph uses a process called gossip about gossip to decide who should create the next block – where “gossip” means quickly exchanging information with a random set of other peers and finding out what they heard from their other peers.
This allows for asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) consensus – meaning if fewer than 1/3rd of nodes malfunction or maliciously send wrong information, consensus can still be reached. Once all have agreed on one version of events, it is posted to the public ledger.
Hashgraph could revolutionize our shared business and social interactions and many things we take for granted today, like Uber or Airbnb. It will also allow us to create decentralized cryptocurrencies, exchanges, stock markets, games, prediction markets, asset registries, and voting systems. By adding hashgraph to your product mix, you’re giving your company an immense advantage over its competitors who are still using old-fashioned databases or blockchain technology.
The Differences Between Blockchain and Hashgraph Technologies
Here’s a list of the key differences between blockchain and hashgraph technologies:
- Hashgraph uses Java and Lisp programming languages, whereas blockchain uses an array of different programming languages.
- It uses a virtual voting consensus mechanism, while blockchain uses proof-of-work or proof-of-stake mechanisms.
- Hashgraph targets 250 000 transactions per second while blockchain can handle 10–25tps for Ethereum and 3–7tps for Bitcoin. This means that hashgraph is over 250x faster than Ethereum and over 400x faster than Bitcoin.
- Hashgraph doesn’t use mining. It means no fees when sending transactions across the network. Using blockchains miners get rewarded with cryptocurrency for each new block added to the chain, which requires paying transaction fees to them.
- It has secure data structures that are resistant to Sybil attacks. ie: (when an entity tries to control the network by creating multiple identities to manipulate the consensus).
- Hashgraph uses digital signatures to verify transactions. It cannot be forged by any person or computer, unlike blockchain, where it is easier to forge transactions using multiple identities to subvert network consensus.
- The hashgraph consensus allows nodes to directly communicate with each other. So, it doesn’t require an additional virtual node making it faster than blockchain at high transaction throughputs because there are no intermediaries/miners that create bottlenecks or slowdowns.
- Hashgraph ensures fairness in how tokens are distributed across the network, whereas some miners on blockchain networks have more computing power than others which can lead to monopolization of cryptocurrency resources. It also provides instant finality of transactions which means that transaction confirmations are received immediately without additional confirmations needed to be done later on.
Which Technology Is Better for Certain Applications or Purposes?
Even though Hashgraph technology is faster than blockchain, there are certain applications that still require more computing power than others. For example, if someone wanted to build an application requiring a high volume of transactions like a cryptocurrency exchange, it would be better to use blockchain technology. The reason is that they can execute more transactions per second than Hashgraph.
However, if someone wanted to create a social media app where users could follow each other or interact with each other more efficiently, using hashgraph instead of blockchain makes sense because the social app won’t be bogged down by transaction throughputs and fees which are problems faced by blockchain-based cryptocurrencies.
A general rule of thumb here is that if you need speed, then use hashgraph technology. While if you need decentralization, then go with blockchain.
What Will the Future of Blockchain and Hashgraph Technologies Look Like?
We have seen the changes metaverse would bring to the world. Similarly, hashgraph and blockchain are all set to create a revolution. It’s widely believed that eventually, hashgraph and blockchain technologies will converge into one single technology. Blockchain is a lot like the internet. It evolved from its humble beginnings to become a way for people to transfer value and data between each other, without an intermediary. Whereas Hashgraph is more like BitTorrent: it allows for faster peer-to-peer interactions such as file-sharing or content distribution.
Many experts believe that cryptocurrencies (open records of transactions between persons) won’t be the only use case of blockchain technology. In the future because there’s no reason why we can’t store files, videos, photos, etc., across the network. There are already projects experimenting with using blockchains for this purpose, such as Filecoin. This means that bitcoin will just be one application of blockchain technology.
Blockchain or Hashgraph
Similarly, many experts believe that instead of cryptocurrencies, applications built on hashgraph will be the only other mainstream use cases of the technology. It’s because they are simply more efficient, especially for social networking or real-time apps that require a high level of scalability and speed. Current blockchains cannot provide these features. Additionally, hashgraph is a better alternative to time-tested databases such as SQL, whereas blockchain isn’t yet suitable for them due to the lack of features such as fixed data structures and transactions finality.
However, it’s possible that both technologies could coexist for quite some time before one eventually becomes obsolete or replaced by another. There’s still plenty of room in the future for either technology, whether businesses, governments, etc. use it, to change the way things are done.
Speaking of latest technologies, Acodez has dealt with a quite a few and is a leading UX agency in India, having experience working with a variety of clients, ranging from leading corporate houses to one-man start-ups, from across the globe. We also are a leading web design company in India, where we handle every aspect of a web project, starting from UX, to UI development, to back-end development to content development and digital marketing. Contact us for more info.
Looking for a good team
for your next project?
Contact us and we'll give you a preliminary free consultation
on the web & mobile strategy that'd suit your needs best.