Most businesses face ongoing pressure to improve their products and services to meet consumer demand.
As an entrepreneur, innovation is not something you can afford to forego. Without the availability of design thinking, none of this is conceivable.
Design thinking solves problems creatively by putting the consumer’s needs first.
It is beneficial to involve different people in specialization in various activities, such as designing and conducting experiments, getting customer feedback, and redesigning the product using creative methods.
Organizations that have adopted various design methodologies admit to progressing from their state of stagnation. The market is dynamic, and new trends are constantly emerging. If you continue to use out-of-date systems, you risk falling behind.
Though it is impossible to pinpoint a single event that gave rise to this idea, the industrial revolution and World War II pushed the frontiers of its development.
The enormous socioeconomic developments at the time led engineers, architects, industrial designers, and cognitive scientists to collaborate to comprehend creative and group problem-solving.
This article will explain design thinking, its guiding principles, various methodologies, and practical applications.
What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is an interactive process that aims to understand your users better by questioning presumptions, redefining challenges, and coming up with creative solutions.
These solutions can then be prototyped and tested.
The overarching objective is to locate other approaches and fixes that are not immediately obvious at your current level of comprehension.
More than just a methodology, design thinking offers a variety of practical techniques to support the application of a completely new style of thinking.
This kind of problem-solving is known as a solution-based approach. Mainly why design thinking is important is:
- Revolves around a strong desire to comprehend the customers we design for goods and services.
- Encourages you to notice and cultivate empathy for the target consumers.
- Improves your capacity for inquiry from your customers and sponsors.
- Helpful in solving ill-defined or unidentified problems.
- New ideas and concepts are explored through prototypes, tests, and trials. This makes sure perfection before releasing a product.
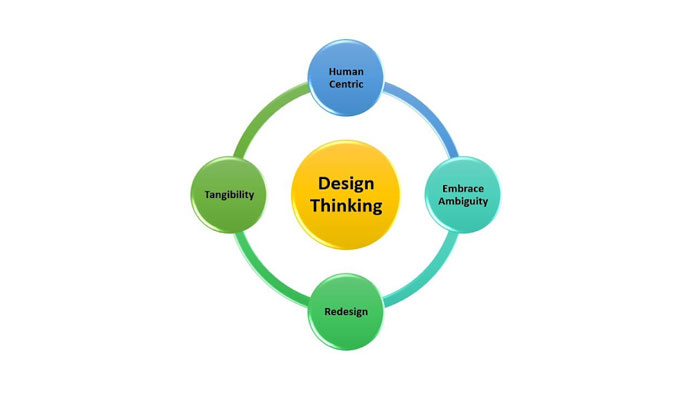
Principles of Design Techniques
Principles of Design Processes – Image Source: LinkedIn
1. Human Centric
Regardless of the context, every design activity is social.
Any social innovation will return us to the “human-centric point of view,” which states that the design of the goods or services should be centered on the users’ needs.
Instead of expecting customers to change their behaviors to fit the product, an entity should base its design decisions on how individuals can, need, and want to execute tasks.
Your team can provide valuable answers to actual issues rather than just clever but pointless goods. You need to empathize with them and draw inspiration from their needs, feelings, and motivations.
Loyalty is created through comprehending and attending to the wants of your customers.
If you intend to introduce anything new and customers have been going through a cycle of changes where you have been sensitive to their needs, they will be willing to try your new services.
2. Embracing Ambiguity
Imagine being at a product launch conference, and someone unexpectedly asks about your product. Ambiguity cannot be avoided or oversimplified; it is an unavoidable part of life.
Being able to see things differently depends on experimenting to the extent of your knowledge and abilities.
Ambiguity in design refers to the capacity to keep competing simultaneously or different ideas in tension. Ambiguity in design practices involves:
- Not knowing all solutions prior to beginning. Start by acknowledging that you can’t possibly know everything.
- Using intuition to explore several approaches to problem-solving or designing a product, service, or experience. This encourages openness to creative thinking.
- Being self-assured enough to hold firm beliefs and ideas while attempting to disprove them. You need to be open-minded to various contradictory theories or methods.
- Holding and advancing concepts that are at odds with how the world and the current frameworks of thought operate.
- Being capable of letting go of specifics when working with complex systems.
The future is uncertain since there are many things we don’t know yet and because many completely different ideas could influence it. Design should be capable of maintaining tension.
The design processes involve working in both simple and complex environments. Despite being in opposing states, you must learn to hold onto both of them.
3. Redesigning
“All design is redesign,” according to the Redesign Rule. While societal conditions and technology may alter and advance, fundamental human needs never change.
Essentially, we change how these demands are met or how we want things to turn out.
All businesses should regularly redesign their websites and applications to stay updated with the latest trends and design guidelines and solve their users’ most urgent concerns.
When should you consider redesigning?
- Dated design. Due to their high friction and a strange sense of misfit with modern norms, outdated interfaces can give the impression that they are unreliable.
- Metrics. You might eventually grow tired of the metrics you’re obtaining and decide it’s time to step things up. Numerous problems, like poor activation, low conversions, and other similar ones, can be solved by a new and improved design.
- Brand updates. This is among the simplest reasons design thinking is essential since there are few fundamental changes to the product. Although relatively simple, it can significantly impact your brand’s market share.
- Negative feedback. It’s essentially free information from genuine users of your website or product which most likely fit neatly into your user persona. Your customers’ problems with your product can be solved by rethinking the experience with them in mind.
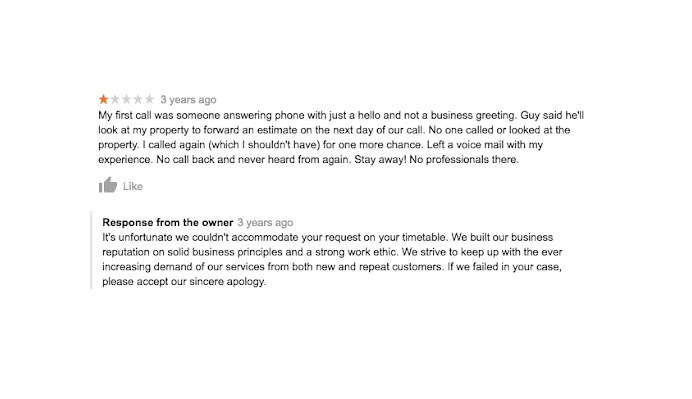
Below is an example of a customer explaining their user experience with an app. The service provider responded positively. If the application gives the same problems to other customers, the service providers should consider redesigning it.
Negative Feedback – Image Source: BrightLocal
4. Tangibility
According to the “tangibility rule,” making concepts concrete always makes it easier for design thinkers to communicate with one another.
Designers can communicate ideas more effectively by giving them a physical embodiment as prototypes.
One should begin experimenting or developing prototypes after gathering ideas. Realizing which concepts are successful and which are not requires experimentation or the creation of prototypes.
Phases of Design Thinking
Phases of Design Methodologies – Image Source: Medium
Before designing anything, you must consider several aspects to ensure a successful product. Failure to do so could expose you to substandard products that would offend your customers.
Different expertise is needed for each step. To avoid difficulties during the final design stage, you should pay close attention to each process.
Each designer should concentrate on the phases listed below.
1. Empathize
A marker will prioritize their interests. If you do this, you will be unable to comprehend any other product usage.
It is a good idea to speak to yourself first, but at the end of the day, you also need to think about your customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders.
The first stage in design thinking is empathy since this ability enables us to comprehend and identify with the emotions of others.
By empathizing with others, we can understand their problems, circumstances, and situations from their point of view and connect with how they might be experiencing them.
You should have the following in mind:
- How does the individual feel?
- What words or actions convey this feeling?
- Can you express their emotions in words?
- What descriptors would you use to express their feelings?
You may find out what the customers want by asking them on various social media channels, reading customer reviews, and observing consumption trends.
A good example is the Uber business. The company has been growing tremendously across the globe. Over 5 billion rides have been completed by Uber worldwide, and the company alone completes 40 million rides every month in the US.
There are already more than 80 countries where Uber is accessible. They try to incorporate their software systems with each country’s national languages and currencies to make the services reliable.
2. Define
Clarity, concentration, and definition are the main concerns of why design thinking is important in the second stage.
To start making sense of the range of options you’re considering, gather all the information you’ve gathered about customer need states, hurdles to achieving those needs, lifestyle realities, and cultural influences in the first stage.
You should consider:
- Recurring themes or patterns are emerging
- Unexpected unmet needs that emerged
- Unforeseen obstacles might divert our attention
- Whether you have the proper questions and if your presumptions about the task at hand require any type of revision
The secret to finding the best ideas and achieving consensus along the road is a solid creative brief developed with both strategic emphasis and innovative creativity.
In other words, everyone involved in the design thinking process will be aware of the aims and purposes of creating the product. It keeps the team on task and speeds up task completion. Additionally, it lessens confusion when working.
As a leader, your job is to ensure that the team focuses on the organization’s culture. More than 70% of employees and leaders agree that culture is more crucial to business success than strategy and operations.
3. Ideate
Now that you have a thorough grasp of your target audience and a clear, well-defined problem to solve, it’s time to start thinking about potential solutions.
This stage calls for a lot of creative thinking. Remember that you are not the only one in the market. You need to develop something original and easy to access and use.
To prevent delays, make sure you have diverse teams assembled and that they can readily cooperate at various levels. You won’t have all the resources, so keep an eye on your suppliers.
Make sure they provide high-quality materials to create durable hardware and software. Before making any sketches or computer designs, you must assess the opportunities’ creative potential and long-term viability if you anticipate any problems.
To ensure successful progress, make the following Mind Mapping, Brainstorming, Sketchnote, Bodystorming, and Inquiry.
Use your intelligence as a measuring stick, your clearly stated brief as a guide, and a S.W.O.T. (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis to determine the strategic viability of each possible option.
4. Prototype
You get to develop problem-solving techniques throughout this stage. The concepts from the earlier stages must now be transformed into tangible items.
These artifacts could be a unique structural innovation, package design system, retail experience, or consumer journey.
It’s reasonable to be unsure whether your target audience will accept the product you’re about to introduce to them at this point.
Do consumer understanding by putting each solution to the test to tops, restrictions, or conceptual problems to ensure there is as little rejection as possible.
In this phase, proposed solutions may undergo several reviews and critiques from the larger team before being modified, redesigned, or discarded.
Failure may arise when things don’t always turn out as expected. If this occurs, you and the team should ask yourselves the following questions:
- What led to failure?
- The solution?
- What was ineffective?
- What can you do better to assist the user the next time?
- Is this approach practical? Is it controllable?
- Were the modifications made with the user in mind?
5. Test
This is one of the reasons why design thinking is essential. After your iterative prototyping and creative creation, look for ways to test quickly and naturally with customers.
Prior testing before making anything available to bigger audiences helps you predict how customers will react to your goods.
If the response is bad, you will need to start over since you can’t release something that will cost your organization money. Negative reviews might potentially harm your brand’s reputation.
Use a “friends and family” strategy if money is short or clients are reluctant to abandon their traditional corporate techniques. The customers you speak with must have a stake in the issue you’re trying to solve.
Open-ended inquiries are geared toward finding solutions, like “What problem could this solve for you?” How might this remedy affect your experience? or “How could it be improved even further as a solution?”
This line of inquiry steers clear responses that discourage iterative improvement and encourages users to enhance the idea or solution in valuable ways.
Examples of Design Thinking
Now that you understand what design thinking is, the principles of design techniques as well as phases of design thinking, let’s go ahead and examine a variety of effectively executed design thinking instances.
Many businesses now emphasize design thinking to compete favorably in the dynamic market. Below are brands that have incorporated the model.
1. Netflix
Netflix Logo – Image Source: Variety
To watch movies initially, customers had to go to a brick-and-mortar store to access DVDs. The procedure was exhausting and intolerable.
By implementing a subscription plan that allows users to watch from the comfort of their homes, Netflix abolished the DVD system.
Around 214 million people paid a monthly subscription to Netflix as of 2021, an increase of more than 16 million customers from the same period the previous year. That number will increase to 670.7 million by 2024.
Evident changes include trailers and the production of original content that is not aired on other traditional networks.
Netflix offers affordable charges, and you can stream as many movies as you want after the subscription.
2. Airbnb
When it first began, Airbnb only made about $200 each week. After some observation, the company’s founders realized that the poor quality of the web advertisement hosts frequently discouraged people from booking rooms.
To understand the problem, they had to incorporate empathy. The creators spent time traveling to each area and picturing what people need in short-term lodging.
They went ahead to Invest in a good camera that would shoot images of what customers wanted to see.
The creators of Airbnb employed design thinking to ascertain why their current audience wasn’t using their services rather than concentrating on expanding their audience.
3. UberEats
It is in our nature to want to purchase food from a food store while relaxing in our own homes. This is doable, thanks to UberEats.
The Walkabout Program at UberEats has designers exploring the places where the firm does business.
They check a variety of things, including infrastructure, delivery procedures, and transportation, as well as food culture and cuisine.
Their immersive study led to several innovations, one of which is the driver app, which focuses on the parking concerns of delivery partners in densely populated urban locations.
alsoRead
https://acodez.in/brand-business-website/
Conclusion
You can use design thinking as a great tool to tackle challenging business issues. However, you must apply it to large and small issues to use it effectively.
The four principles, human-centric, ambiguity, redesign, and tangibility, are essential in design thinking.
The five design thinking steps of empathizing, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing should be carried out sequentially. If you don’t follow them strategically, you’ll end up with undesirable results.
Businesses who have taken time integrating design may witness how it has raised consumer and customer retention. Any organization wants to be profitable, and if you don’t care about your customers’ needs, you won’t be able to do that.
Acodez is a leading web design company in India offering all kinds of web design and development solutions at affordable prices. We are also an SEO and digital marketing agency offering inbound marketing solutions to take your business to the next level. For further information, please contact us today
Looking for a good team
for your next project?
Contact us and we'll give you a preliminary free consultation
on the web & mobile strategy that'd suit your needs best.